Automatic background verification [PREMIUM ONLY]
NOTE: Note: Automatic background verification of repositories and wikis was added in GitLab EE 10.6 but is enabled by default only on GitLab EE 11.1. You can disable or enable this feature manually by following these instructions.
Automatic backgorund verification ensures that the transferred data matches a calculated checksum, proving that the content on the secondary matches that on the primary. Following a planned failover, any corrupted data may be lost, depending on the extent of the corruption.
If verification fails on the primary, this indicates that Geo is successfully replicating a corrupted object; restore it from backup or remove it it from the primary to resolve the issue.
If verification succeeds on the primary but fails on the secondary, this indicates that the object was corrupted during the replication process. Geo actively try to correct verification failures marking the repository to be resynced with a backoff period. If you want to reset the verification for these failures, so you should follow these instructions.
If verification is lagging significantly behind replication, consider giving the node more time before scheduling a planned failover.
Disabling or enabling the automatic background verification
The following commands are to be issues in a Rails console on the primary:
# Omnibus GitLab
gitlab-rails console
# Installation from source
cd /home/git/gitlab
sudo -u git -H bin/rails console RAILS_ENV=productionTo check if automatic background verification is enabled:
Gitlab::Geo.repository_verification_enabled?To disable automatic background verification:
Feature.disable('geo_repository_verification')To enable automatic background verification:
Feature.enable('geo_repository_verification')Repository verification
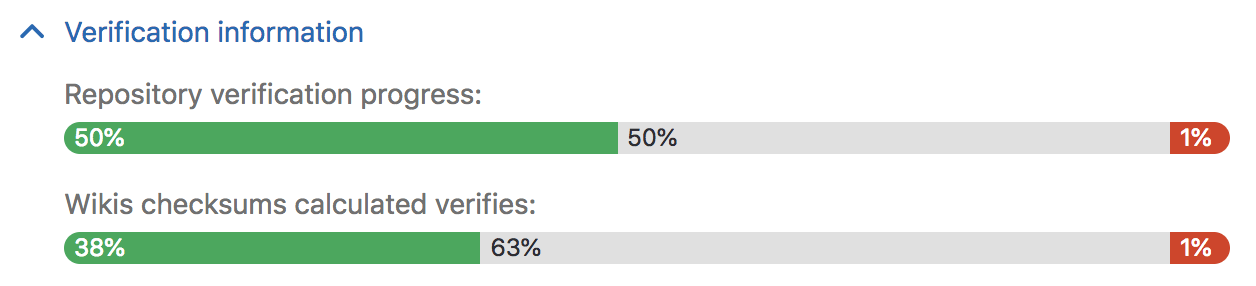
Navigate to the Admin Area > Geo dashboard on the primary node and expand the Verification information tab for that node to view automatic checksumming status for repositories and wikis. Successes are shown in green, pending work in grey, and failures in red.
Navigate to the Admin Area > Geo dashboard on the secondary node and expand the Verification information tab for that node to view automatic verifcation status for repositories and wikis. As with checksumming, successes are shown in green, pending work in grey, and failures in red.
Using checksums to compare Geo nodes
To check the health of Geo secondary nodes, we use a checksum over the list of
Git references and their values. The checksum includes HEAD, heads, tags,
notes, and GitLab-specific references to ensure true consistency. If two nodes
have the same checksum, then they definitely hold the same references. We compute
the checksum for every node after every update to make sure that they are all
in sync.
Reset verification for projects where verification has failed
Geo actively try to correct verification failures marking the repository to be resynced with a backoff period. If you want to reset them manually, this rake task marks projects where verification has failed or the checksum mismatch to be resynced without the backoff period:
For repositories:
Omnibus Installation
sudo gitlab-rake geo:verification:repository:resetSource Installation
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rake geo:verification:repository:reset RAILS_ENV=productionFor wikis:
Omnibus Installation
sudo gitlab-rake geo:verification:wiki:resetSource Installation
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rake geo:verification:wiki:reset RAILS_ENV=productionCurrent limitations
Until issue #5064 is completed, background verification doesn't cover CI job artifacts and traces, LFS objects, or user uploads in file storage. Verify their integrity manually by following these instructions on both nodes, and comparing the output between them.
Data in object storage is not verified, as the object store is responsible for ensuring the integrity of the data.